How to Use SFC and DISM Commands for Effective Troubleshooting
Introduction
Windows relies on thousands of critical system files to function correctly. When these files become corrupted, missing, or modified, it can lead to performance issues, application crashes, update failures, or even prevent Windows from booting entirely.
Typical symptoms of system file corruption include:
- Slow performance or frequent freezes
- Apps failing to launch without clear error messages
- Windows Update errors (e.g., 0x800f081f)
- Features like search, Start Menu, or Settings not working
- Random restarts or boot loops
Fortunately, Windows includes built-in tools — System File Checker (SFC) and Deployment Imaging Service and Management Tool (DISM) — that can scan and repair damaged files without third-party software.
This guide explains how to use them step-by-step, when to run each tool, and what to do if they fail.
Common Causes of System File Corruption
Understanding why files become damaged can help you prevent future issues.
| Cause | Details |
|---|---|
| Failed Windows Updates | Updates stop midway, leaving incomplete or mismatched system files. |
| Forced Shutdowns / Power Loss | Interrupting Windows during writes can corrupt active files. |
| Malware Infection | Malicious software modifies or deletes protected system files. |
| Storage Device Issues | Bad sectors or SSD/HDD wear cause read/write errors that damage files. |
| Third-Party Software Conflicts | Over-aggressive security or “optimizer” tools quarantine/delete legitimate files. |
| Unsafe Tweaks / Registry Changes | Poorly designed cleaners remove required DLLs or registry entries. |
| Driver or Service Conflicts | Incompatible drivers or background services disrupt core processes. |
| File System / Registry Inconsistencies | Crashes or improper shutdowns leave NTFS or the registry in an inconsistent state. |
💡 Tip: You can check your storage health using free tools like CrystalDiskInfo or manufacturer diagnostic utilities.
What Is SFC (System File Checker)?
SFC is a command-line utility built into Windows that scans protected system files and replaces incorrect, corrupted, or missing versions with a cached copy stored locally.
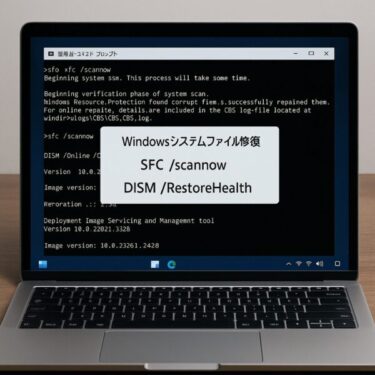
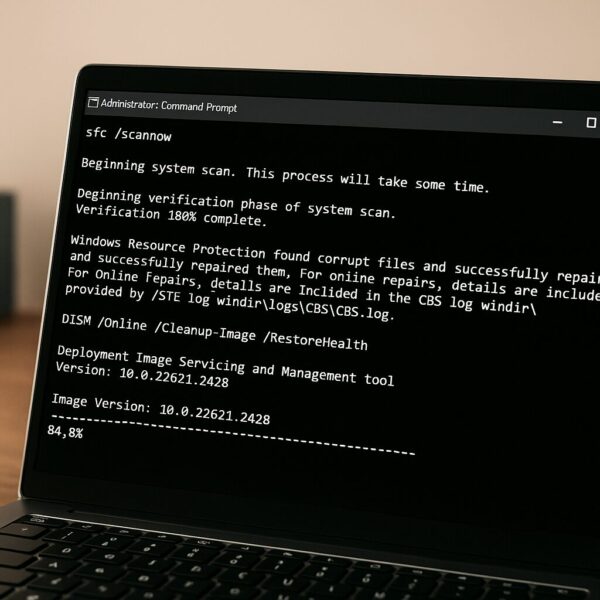
How to Run SFC
①Open Command Prompt as Administrator
②Search for “cmd” in the Start Menu
③Right-click and select Run as administrator
Type:
- Press Enter and wait for the scan to reach 100%.
Possible Results
- Windows Resource Protection did not find any integrity violations
→ No issues detected. - Windows Resource Protection found corrupt files and successfully repaired them
→ Problems were found and fixed. - Windows Resource Protection found corrupt files but was unable to fix some of them
→ SFC could not repair everything — proceed with DISM.
💡 Best Practice: Avoid using the PC during the scan to prevent interference.
What Is DISM and When to Use It?
DISM is a more advanced tool that repairs the underlying Windows image itself — the source SFC uses to restore files. If the image is damaged, SFC will fail.
How to Run DISM
- Open Command Prompt (Admin).
- Run these commands in sequence:
Step 1 – Quick Health Check
Step 2 – Deep Scan
Step 3 – Repair the Image
3. Once complete, run sfc /scannow again to verify repairs.
💡 Important: DISM needs an internet connection to download fresh files from Microsoft’s servers. If your PC is offline, you can use an installation ISO as the source with:
(Replace X: with your media drive letter.)
Recommended Execution Order
- Minor issues or suspected corruption: Run SFC first.
- After major updates or persistent errors: Run DISM first, then SFC.
- If Windows won’t boot normally: Boot into Safe Mode with Networking and run DISM + SFC.
Precautions Before Running Repairs
- Do not use the PC while scans are running — background activity can cause false positives or failures.
- Keep laptops plugged in to avoid shutdowns.
- Ensure adequate free disk space (at least 10 GB recommended).
- Scan for malware first — if malware is active, repairs may be overwritten immediately.
⚠ Note: Ignoring these precautions may lead to incomplete repairs or further instability. DISM in particular requires a stable internet connection; if your connection drops mid-repair, you might need to restart the process. Also, if your storage device is failing, no software-based repair will be permanent — check disk health and back up your data before attempting fixes.
Common Errors and Fixes
| Error | Solution |
|---|---|
| 0x800f081f | Run DISM with the /Source option using installation media or an ISO image. |
| Some files could not be repaired | Run DISM first, then re-run sfc /scannow to verify repairs. |
| Scan stops midway | Run in Safe Mode or perform a disk check using chkdsk /f. |
| Access denied | Ensure Command Prompt is launched as Administrator. |
| 0x80070490 | Use DISM with the /RestoreHealth option, then run SFC. |
| 0x80070057 | Free up disk space, then retry the scan or repair process. |
Preventing Future Corruption
- Install Windows Updates regularly.
- Avoid forced shutdowns during updates or installs.
- Limit the number of startup programs.
- Use a UPS to protect against power loss.
- Run SFC/DISM health checks every 6–12 months.
Bonus: Advanced Troubleshooting Tips
- Check CBS Logs: After running SFC, check C:\Windows\Logs\CBS\CBS.log for details.
- Combine with CHKDSK: If disk errors exist, run chkdsk C: /f /r before SFC/DISM.
- Offline Repair: Boot from installation media, open Command Prompt, and run:
- Third-Party Alternatives: Tools like Macrium Reflect (Free) can back up your system before major repairs.
Conclusion
System file corruption is one of the most common causes of Windows instability, but it’s also one of the easiest to fix using the built-in SFC and DISM commands.
By following the correct order — DISM when needed, then SFC — and taking precautions before running repairs, you can often restore your PC’s stability without reinstalling Windows.
Bookmark this guide so you’ll have it ready the next time your system starts acting up — and remember, prevention is always easier than recovery.
✔️You might also find these helpful:
▶︎How to Fix Windows C Drive Permission Errors (Full Recovery Guide)
▶︎Google Drive for Desktop Not Working on Windows – Real Fixes That Work
▶︎How to Fix Windows Error Code 0x80070057 on Windows 11 — Complete Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
💡 Looking for more tips? Check out our full list of Windows Help Guides.